NetworkForwarder
Description
This module forwards messages that are emitted in the system over NUClearNetwork.
Messages that are emitted are sent to the target when they are enabled in the configuration file.
The configuration file is able to set either true for a message type in which case it will attempt to send every single packet or you can set a number and it will rate limit that packet.
The forwarder will split messages rate limiting by an id field if they have one
Emits
Network emits every message that is in the configuration over NUClearNet to the target
NUClearNet
This module is responsible for connecting the system to the NUClear Network. In the configuration you must set a name, broadcast address and port. By setting these three the network will connect and be able to communicate with other NUClearNet systems that are on the same network.
Name
If the name is left as an empty string in the configuration, the system will use the current host name as the name of the NUClearNet node.
Address
The NUClearNet system can take an IP address or a dns name as the address. The address is able to resolve to either IPv4 or IPv6 address. There are three main ways you can configure the network and use it.
Unicast Mode
In Unicast mode, you connect from this device to another device on a specific other system. This address may also be 127.0.0.1 if you wish to only connect to other NUClearNet binaries on the same system.
In Unicast mode, you set the IP address here to the IP address of the other system you wish to connect to and on that system set the IP address of this system.
This form of networking is useful when you are debugging and wish to make a small isolated NUClearNet system.
Broadcast Mode
In broadcast mode, you set the address to the broadcast IP of your network (e.g. 192.168.1.255 for the network 192.168.1.0/24). In this mode you will connect to all other systems that are running on that same network. In general you should prefer multicast mode over this mode so that you only send packets to systems that are specifically part of the NUClearNet node rather than sending to all computers on the network and using up the bandwidth.
Multicast Mode
In multicast mode you set either an IPv4 or IPv6 multicast address. Then provided your network correctly routes multicast packets it will connect to all other NUClearNet nodes that share the same multicast address. The default address for this is 239.226.152.162
Port
The default port for NUClearNet is 7447. You can use different ports if you want to make several distinct NUClearNet networks on the same device.
PlotJuggler
Description
This module allows for sending data from NUbots to PlotJuggler for plotting in real time. It does this by listening for DataPoint messages (what we use for plotting in NUsight), transforming them to a suitable format and sending them to PlotJuggler via UDP.
Usage
To plot data from a role you're working on using PlotJuggler, do the following.
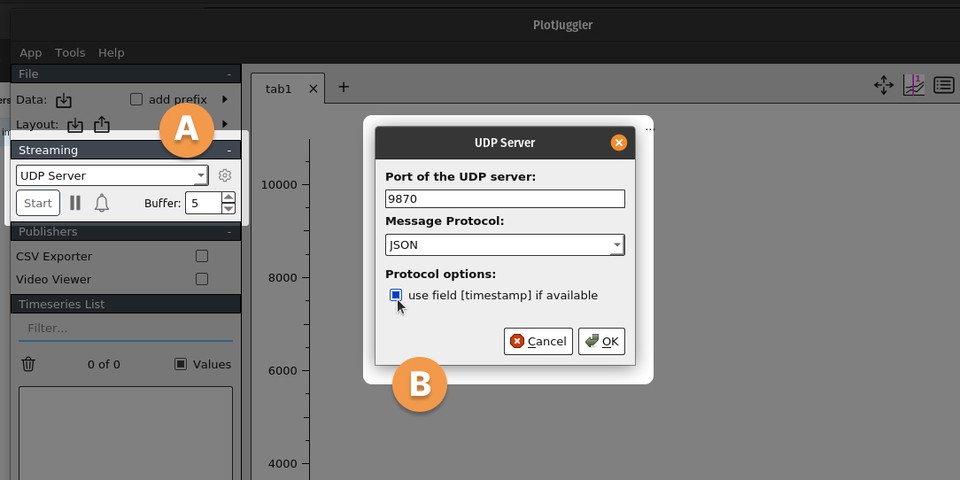
Launch PlotJuggler and start the UDP server.
![Screenshot of PlotJuggler showing UDP server details]()
A. Under the Streaming section at the left of the PlotJuggler UI, select "UDP Server" and click "Start".
B. In the window that pops up, enter a port, select "JSON" for Message Protocol, and check the box to use the timestamp field if available. Take note of the port and click "OK".
Add the
network::PlotJugglermodule to the role you're working on.Update the
PlotJuggler.yamlconfig file.- Set
forward_datapointsto true to enable forwarding of data to PlotJuggler. - Under
udp_server, setip_addressandportto the UDP server details from PlotJuggler.ip_addressshould be the address of the computer running PlotJuggler, or127.0.0.1if you're running PlotJuggler on the same computer as the role binary.
- Set
In your role, anywhere you want to plot data:
Include the
graph()helper:// In the includes section#include "utility/nusight/NUhelpers.hpp"// In the module namespace, to use `graph()` without specifying the namespace prefix every timeusing utility::nusight::graph;Call
graph()with the label and values you want to plot, andemit()the result:// Plotting a single valueemit(graph("Distance to ball", distance_to_ball));// 2-4 values will be labelled "x", "y", "z", "w" automaticallyemit(graph("Gyro", my_gyro_data.x(), my_gyro_data.y(), my_gyro_data.z()));// 5 or more values will be labelled "s0", "s1", "s2", ..., "s[n-1]" automaticallyemit(graph("My data", s0, s1, s2, s3, s4));
Build and run your role
Data should start appearing in the PlotJuggler sidebar when the role is running. To plot a data point, drag its label from the sidebar to the graph space at the right.
Note If you're not seeing data in PlotJuggler, double check that the UDP server is running,
PlotJuggler.yamlhas the right configuration, and your role is sending data. You can also set thesend_debug_wavesconfig option totrueto send sample data to PlotJuggler to test the connection.
Consumes
message::eye::DataPoint- listens for these from the rest of the codebase, transforming and forwarding them to PlotJuggler
Emits
message::eye::DataPoint- when debug waves are enabled for testing the connection to PlotJuggler- JSON-formatted packets to PlotJuggler via UDP
Dependencies
- JSON for modern C++ library
RobotCommunication
Description
This module adds a communication schema that conforms to the official robocup spec. It allows the robots to use this schema for internal communication.
The Robocup message is created, and emitted to other robots over UDP. All UDP messages are received by every robot in the network.
UDP messages that have been emitted by the receiving robot are filtered out.
The information that has been received over UDP is then emitted locally.
Usage
Add this module to get information about other robots.
Consumes
message::input::RoboCupwhich contains data about the robot, including its state, current position, projected position and its view of the other robots.message::behaviour::state::WalkStatewhich contains data about the robot's current movement.message::input::GameStatewhich contains the current state of the game and penalised robots.message::input::Sensorswhich contains data from the robot's sensors, used to calculate its world position.message::localisation::Ballwhich contains information about the estimated position and velocity of the ballmessage::localisation::Fieldwhich contains information to convert values from world to field spacemessage::skill::Kickwhich contains the direction and target of the robot's kick
Emits
message::input::RoboCupvia UDP.message::input::RoboCupvia local.